Carbon Footprint
Square Footprint
Fossil Fuel Footprint
Carbon Footprint
Square Footprint
Fossil Fuel Footprint

653 kg CO2e / MWh
3,739 ft2 / MWh / 100 Yrs
77.0% Fossil Fuels

653 kg CO2e / MWh
3,739 ft2 / MWh / 100 Yrs
77.0% Fossil Fuels


If the average US home's annual electricity (10.715 MWh) was powered by the India Power Grid, it would use:
823
Gallons of Gasoline Equivalent
6,997
kg CO2e

If the average US home's annual electricity (10.715 MWh) was powered by the India Power Grid, it would use:
823
Gallons of Gasoline Equivalent
6,997
kg CO2e
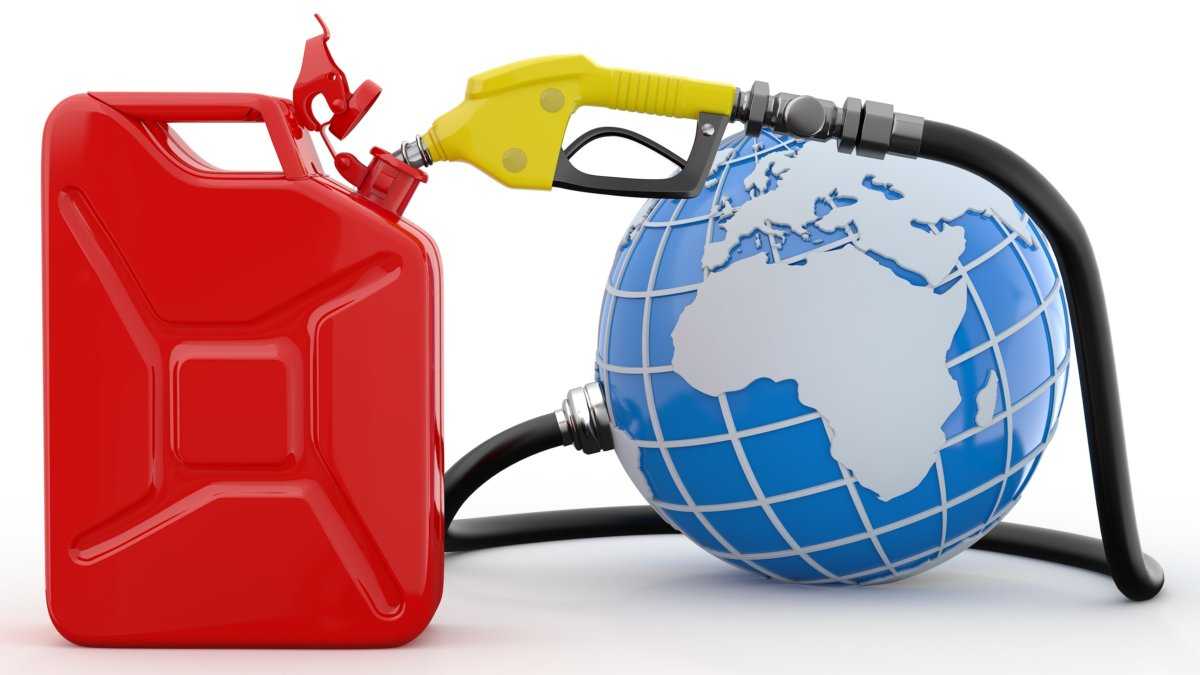
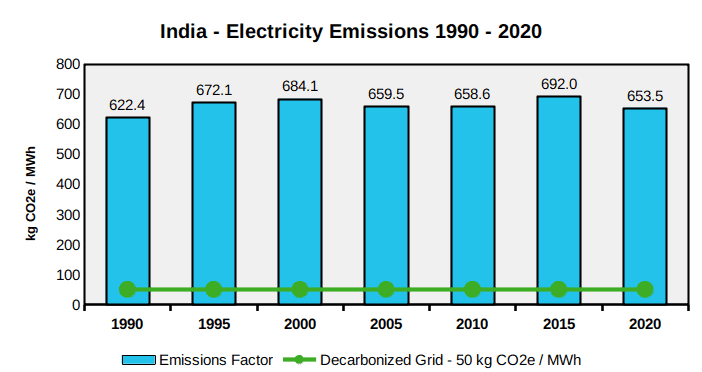
In 2020, the Carbon Footprint of the average electricity generated in India is 653 kg CO2e per Megawatt Hour (MWh). The greenhouse gas emissions of the India Power Grid are 41.7% higher than the world average of electricity generation.
In 2020, 77.0% of India’s electricity came from fossil fuels, 20.3% came from renewables, and 2.7% came from nuclear. Since 1990, India has increased its grid emissions by 5.0%. India relies on coal power for 72.5% of its electricity, which generates 95.7% of its grid emissions. Average electricity emissions in India are 13.1 times higher than a decarbonized grid, which emits 50 kg CO2e / MWh.


If the average US home's annual electricity (10.715 MWh) was powered by the India Power Grid for 100 years, it would use:
278
Parking Spaces Equivalent
40,063
ft2

If the average US home's annual electricity (10.715 MWh) was powered by the India Power Grid for 100 years, it would use:
278
Parking Spaces Equivalent
40,063
ft2
In 2020, the Square Footprint of the average electricity generated in India is 3,739 ft2 per Megawatt Hour (MWh) over 100 years. The land use of the India Power Grid is 69.0% higher than the world average of electricity generation.
Data and Assumptions
Carbon Footprint:
| Fuel Source | % of Grid Electricity | Source Emissions (kg CO2e / MWh) | Weighted Emissions (kg CO2e / MWh) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coal | 72.5% | 863.0 | 625.32 |
| Hydro | 10.4% | 20.5 | 2.13 |
| Natural Gas | 4.2% | 486.0 | 20.60 |
| Wind | 4.1% | 13.0 | 0.53 |
| Solar PV | 3.8% | 23.0 | 0.88 |
| Nuclear | 2.7% | 13.0 | 0.35 |
| Biomass | 1.9% | 52.0 | 1.01 |
| Oil | 0.3% | 840.0 | 2.57 |
| Waste | 0.1% | 82.4 | 0.08 |
| Geothermal | 0.0% | 36.7 | 0.00 |
| Solar Thermal | 0.0% | 28.0 | 0.00 |
| Tidal | 0.0% | 8.0 | 0.00 |
| Other Unknown Fuels | 0.0% | 653.5 | 0.00 |
| Total | 100.0% | 653.47 |
- The Carbon Footprint of all energy sources except for Solar is based on NREL (2021), which uses cradle to grave emissions factors. The share of energy sources is based on the International Energy Agency (IEA, 2022) with 2020 data. See the table below for individual source emission values and weights.
- The value for “Supercritical Pulverized Coal” in NREL (2021) is assumed for “Coal” in the IEA Database.
- The average value for “Natural Gas” of all technologies from NREL (2021) is assumed for “Natural Gas” in the IEA Database.
- The value for “Oil” in NREL (2021) is used for “Oil” in the IEA Database.
- The value for “Light Water Reactors” in NREL (2021) is used for “Nuclear” in the IEA Database.
- The average value for “Wind” for all technologies in NREL (2021) is used for “Wind” in the IEA Database.
- The average value for “Hydropower” for all technologies in NREL (2021) is used for “Hydro” in the IEA Database.
- The average value for “Biopower” in NREL (2021) is assumed for “Biofuels” in the IEA Database.
- The average value for “Geothermal” for all technologies in NREL (2021) is used for “Geothermal” in the IEA Database.
- The average value for “Concentrating Solar Power” in NREL (2021) is used for “Solar Thermal” in the IEA Database. Value is not adjusted for average solar radiation of each country because a reference solar radiation value is not given.
- The value for “Waste” in the IEA Database is based on Pfadt-Trilling et al. (2021), who performed a lifecycle of waste, including diverted waste streams from energy recovery, or Waste-to-Energy. The study found a net emission of 0.0824 kg CO2e / kWh, or 82.4 kg CO2e / MWh, which is used for the emission factor or waste energy. Value does not include methane recovery.
- The value for “Ocean” in NREL (2021) is used for “Tide” in the IEA Database.
- The weighted average value for all energy sources is used for “Other Sources” in the IEA Database. These sources primarily include energy recovery and purchases of waste heat from other industrial processes. “Other Sources” only made up 0.18% of world energy generation in 2019.
- See the “Further Resources” Section below for individual assumptions made for each additional fuel source.
- The carbon footprint of solar PV is based on the harmonized value of 25 g CO2e / kWh for monocrystalline solar PV reported by Louwen et al. (2016). Original value is based on Wetzel & Borchers (2015).
- Solar radiation value of 1,845 kWh m2 / yr is based on the Global Solar Atlas (2022) Global Horizontal Irradiation average for all of India. Average raster file value was obtained using QGIS (2022). Note this value is likely an underestimation of installed solar capacity, as solar is more likely to be installed in areas with higher solar radiation.
- Value adjusted to 23.0 g CO2e / kWh to adjust for 1,700 kWh / m2 / yr solar radiation reference value used in Wetzel & Borchers (2015).
- For further details see the Solar Panels Carbon Footprint & Environmental Impact Page.
Land Use:
| Fuel Source | % of Grid Electricity | Source Emissions (ft2 / MWh / 100 Yrs) | Weighted Emissions (ft2 / MWh / 100 Yrs) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coal | 72.5% | 4,839.0 | 3,506.3 |
| Hydro | 10.4% | 182.0 | 18.9 |
| Natural Gas | 4.2% | 845.0 | 35.8 |
| Wind | 4.1% | 14.1 | 0.6 |
| Solar PV | 3.8% | 74.7 | 2.8 |
| Nuclear | 2.7% | 140.0 | 3.7 |
| Biomass | 1.9% | 8,716.0 | 169.4 |
| Oil | 0.3% | 603.0 | 1.8 |
| Waste | 0.1% | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Geothermal | 0.0% | 55.3 | 0.0 |
| Solar Thermal | 0.0% | 74.7 | 0.0 |
| Tidal | 0.0% | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Other Unknown Fuels | 0.0% | 3,739.4 | 0.0 |
| Total | 100.0% | 3,739.4 |
- The Square Footprint of all energy sources except for Solar is based on Trainor et al. (2016). The share of energy sources is based on the International Energy Agency (2022) with 2020 data. See the table below for individual source emission values and weights.
- Land use for nonrenewable resources is based on 100 years of resource extraction. Land use of renewable resources stays constant, and the disturbed land only happens once in the lifecycle of energy production. Thus, as additional renewable energy capacity is added, land use change occurs, but only during installation, and not replacement.
- The values for “Underground Coal” and “Surface Coal” from Trainor et al. (2016) are assumed for “Coal” in the IEA Database. Mining type percentage based on Global Energy Monitor (2022) who states that 51.07% of global coal mines use Surface Coal.
- The values for “Conventional Natural Gas,” “Shale Gas,” and “Tight Gas” from Trainor et al. (2016) are assumed for “Natural Gas” in the IEA Database. Based on EIA (2016), world Shale Gas production was 42 billion cubic feet per day (bcf/d), out of a total of 342 bcd/f, which totals 12.3%. Exact numbers are not available for the other fuel sources, and therefore a value of 10% is assumed for Coalbed Methane and Tight Gas combined. Therefore, Conventional Natural Gas is assumed to contribute 77.7% of world natural gas production in 2015.
- The value for “Conventional Oil” of 0.56 km2 / TWh / yr (0.56 m2 / MWh/ yr) in Trainor et al. (2016) is assumed for “Oil” in the IEA Database.
- The value for “Nuclear” in Trainor et al. (2016) is assumed for “Nuclear” in the IEA Database. 2020 value is based on 2019 generation.
- The value for “Wind” in Trainor et al. (2016) is assumed for “Wind” in the IEA Database.
- The value for “Hydropower” in Trainor et al. (2016) is assumed for “Hydro” in the IEA Database.
- The value for “Biomass” in Trainor et al. (2016) is assumed for “Biofuels” in the IEA Database.
- The value for “Geothermal” Trainor et al. (2016) is assumed for “Geothermal” in the IEA Database.
- The value for “Waste” in the IEA Database is assumed to be 0, as waste energy recovery does not contribute to land use change, and the benefits are considered to be ancillary to the primary land use for waste storage.
- The value for “Tide” in the IEA Database is assumed to be 0, as it does not affect land use above sea level.
- The weighted average value for all energy sources is used for “Other Unknown Fuels” in the IEA Database.
- See the Further Resources Section below for individual assumptions made for each additional fuel source.
- The Square Footprint of “Solar PV” and “Solar Thermal” is based on Van de Ven et al. (2021) for the center of India at 22.89 degrees of latitude (Harvard WorldMap, 2021) at 1,845 kWh / m2 / yr solar radiation. See the Solar Land Use Page for further details.
- Solar radiation value of 1,845 kWh m2 / yr is based on the Global Solar Atlas (2022) Global Horizontal Irradiation average for all of India. Average raster file value was obtained using QGIS (2022). Note this value is likely overestimates the emission factor of installed solar capacity, as solar is more likely to be installed in areas with higher solar radiation.
- Assume that 12.3% of installed solar capacity is for rooftop solar PV, based on the average of the middle scenarios presented in Jan Van de Ven (2021). Rooftop solar is considered to have a land use of 0.
- Square Footprint of a Parking Space is 144 ft2, based on the average dimensions stated by Franklin Street (2019).
- The data presented does not factor energy imports or exports from other countries.
- Average 2020 US Household annual electricity of 10,715 kWh is based on EIA (2021A).
- Carbon Footprint of gasoline is 8.50 kg CO2e / gallon, based on EIA (2021B).
- Coal Power Carbon Footprint & Environmental Impact
- Geothermal Power Carbon Footprint & Environmental Impact
- Hydropower Carbon Footprint & Environmental Impact
- Natural Gas Power Carbon Footprint & Environmental Impact
- Nuclear Power Carbon Footprint & Environmental Impact
- Solar Land Use
- Solar Panels Carbon Footprint & Environmental Impact
- Wind Power Carbon Footprint & Environmental Impact
References
EIA: US Energy Information Administration. (2021A). How Much Electricity Does an American Home Use?. See Link to Source
EIA: US Energy Information Administration. (November 18, 2021B). Carbon Dioxide Emissions Coefficients by Fuel. See Link to Source
EIA: US Energy Information Administration. (August 15, 2016). Shale gas production drives world natural gas production growth. See Link to Source
Franklin Street. (May 23, 2019). How Large is a Parking Space? See Link to Source
Global Energy Monitor. (January, 2022). Global Coal Mine Tracker – Summary Tables – Summary Table 12 – Coal Production By Mine Type (Surface, Underground). See Link to Source
Global Solar Atlas. (2022). India Global Horizontal Irradiation. See Link to Source
Harvard WorldMap. (April 8, 2021). County Centroids. See Link to Source
IEA: International Energy Agency. (2022). Electricity – Electricity Generation by Source. See Link to Source
Louwen, A., Van Sark, W. G., Faaij, A. P., & Schropp, R. E. (2016). Re-assessment of net energy production and greenhouse gas emissions avoidance after 40 years of photovoltaics development. Nature Communications, 7(1), 1-9.
NREL: National Renewable Energy Laboratory. (2021). Life Cycle Assessment Harmonization. See Link to Source
QGIS.org, 2022. QGIS Geographic Information System. QGIS Association. http://www.qgis.org

